[ad_1]
denisgo
By Sonal Desai, Ph.D., Chief Funding Officer, Franklin Templeton Mounted Revenue | Angelo Formiggini, Economist & Worldwide Analysis Analyst, Franklin Templeton Mounted Revenue | Nikhil Mohan, Economist, Franklin Mounted Revenue | Rini Sen, Economist & Analysis Analyst, Franklin Templeton Mounted Revenue
Government abstract
US financial assessment
US financial system: A flashback to the Nineteen Nineties mushy touchdown

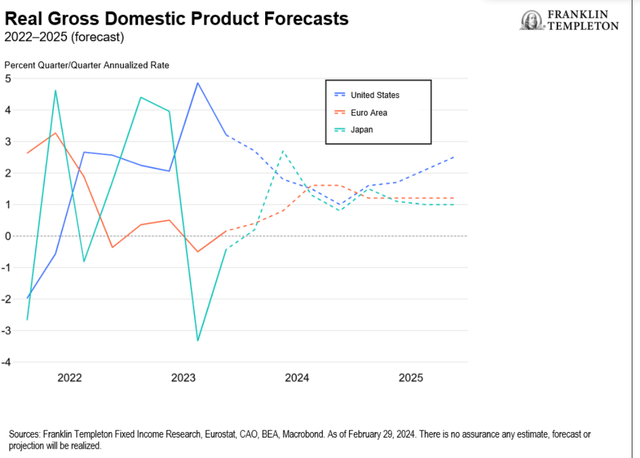
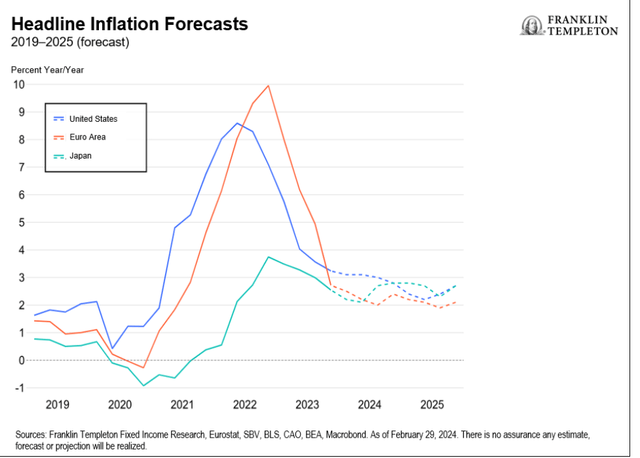
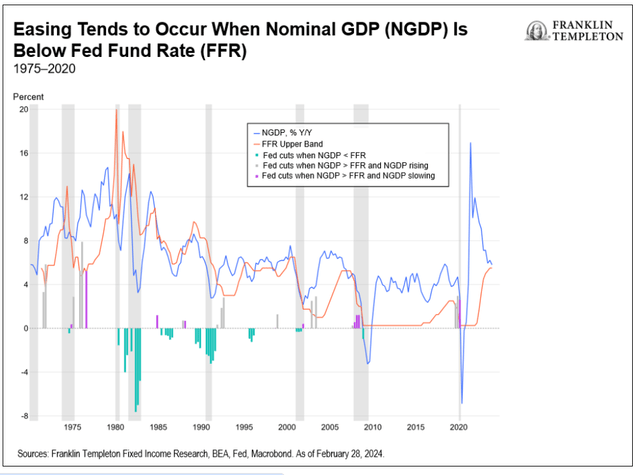
The US financial system continues to exhibit indicators of energy. Though family spending slowed via 2023, year-over-year (y/y) progress charges remained at their longer-term averages. A still-robust labor market, strong wage and actual disposable revenue progress, together with robust family steadiness sheets, ought to stay supportive of consumption going ahead, albeit slower than in 2023 owing to a considerably smaller financial savings cushion. Whereas labor demand has slowed resulting from a decline in job openings, payroll progress continues to oscillate round its longer-term common. Extra demand for labor, at 2.8 million, continues to be about 1.5 million above pre-pandemic ranges. Nonetheless, the slowdown in labor-force participation might fear the Fed by way of the upward strain this might placed on wages. The January inflation prints function a reminder that the potential for inflation flare-ups stays. Equally regarding is the rise within the prices-paid measures for each the manufacturing and companies elements of the Institute of Provide Administration report. Small companies have additionally more and more thought-about worth hikes and wage will increase. Due to this fact, we expect the Fed can maintain rates of interest excessive for some time longer to make sure inflation is sustainably making its means all the way down to 2%. First Fed charge lower almost definitely postponed till July on the earliest, in our view. Most easing cycles for the reason that Volcker-led Fed have began with y/y nominal gross home product (GDP) progress beneath the extent of the funds rate-as Bloomberg columnist Cameron Crise famous. The 1995 cycle implies easing might not begin earlier than September, which looks like an affordable risk as markets too have at present assigned the best likelihood for a primary charge lower in September. Nonetheless, nominal progress will seemingly slip beneath the coverage charge by the second quarter, leaving July as a risk for a charge lower, in our view. Actual charges may even seemingly be pushing above 3% by then. How deep the Fed cuts within the coming easing cycle will rely upon the character of the financial “touchdown.” Productiveness progress, and in impact, the Fed’s view of the true impartial charge (R*) are necessary determiners of ahead coverage. A rerun of the mid-Nineteen Nineties-a scenario the place productiveness progress does certainly take off (nascent indicators of that occurring), which might additionally suggest a better R*-could make expectations of 150-200 foundation factors of charge cuts over the subsequent couple of years appear extreme.
European financial outlook
Euro-area financial system: cautiously optimistic

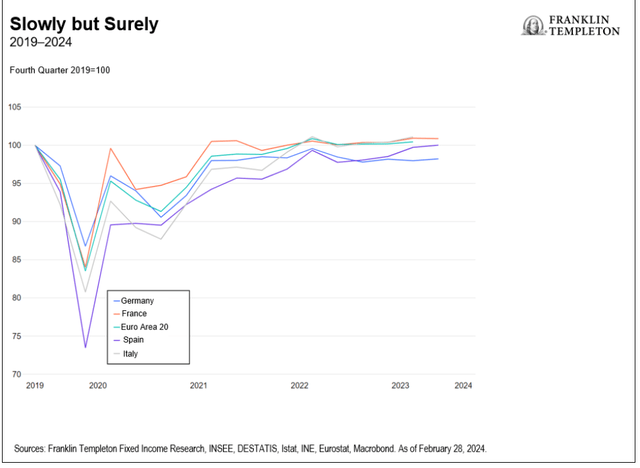
The financial system is exhibiting timid indicators of enchancment. Eurozone progress was stagnant over the fourth quarter of 2023 (This autumn), supported by upside surprises in Spain and Italy, whereas France sidelined and Germany recorded a contraction. We anticipate a gradual, consumption-driven restoration all through the primary half 2024. Non-public consumption is fragile, however on the mend. Shopper confidence stays subdued, as financial uncertainty weighs on spending intentions. Going ahead, a still-strong labor market, strong wage progress and declining inflation ought to help actual incomes and a consumption restoration. The job market is resilient and present process a gradual rebalancing. Employment progress continued to outpace GDP progress in This autumn, with the unemployment charge remaining at historic lows. The labor market is now witnessing a gradual cyclical rebalancing. Hiring is prone to sluggish within the quarters forward, which is symptomatic of excessive employment and rising labor prices. This could assist stabilize wages. The credit score drag on the financial system has seemingly peaked and can diminish going ahead. Credit score situations have stabilized, and credit score flows ought to decide up from the very weak ranges witnessed within the earlier quarters. It’s clear to us that the financial coverage transmission mechanism has labored, and its reversal will ease the compression in investments. Nonetheless, the timing of this stays unsure. Sustainable deflation relies on an unsure wage and productiveness outlook. Easing vitality and items costs have largely supported the decline in headline inflation. In the meantime, companies inflation has proved sticky, supported by wage will increase. Rising wages and declining labor productiveness will seemingly proceed to place upward strain on unit labor prices. The European Central Financial institution (ECB) is prone to proceed with warning. The main target will stay on second-round results, particularly on traditionally excessive wage inflation, companies’ revenue margins and weak productiveness. Policymakers will seemingly search reassurance of wage progress stabilization earlier than embarking on financial coverage easing and can proceed cautiously in 2024.
Japan financial outlook
Japan’s financial system: nearly there

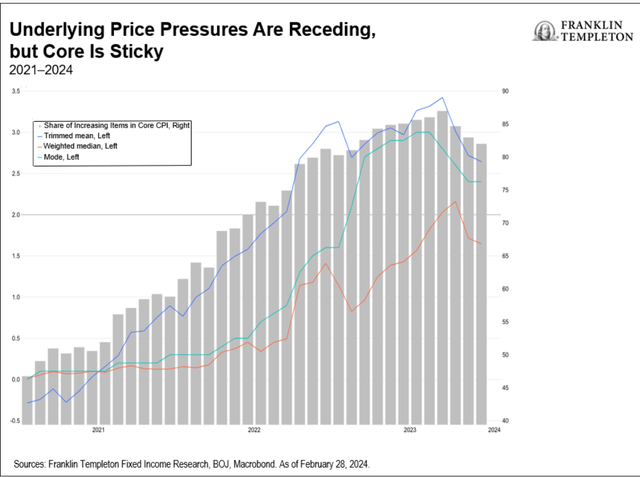
Development has been sluggish with a technical recession in This autumn. The primary quarter of 2024 will seemingly proceed to be on weak footing, owing to repercussions from the Noto earthquake and auto manufacturing disruptions. However the outlook is just not fully bleak. We anticipate a modest restoration within the second half of 2024 as stronger wage positive aspects cushion non-public consumption, and personal capital expenditure (CAPEX) appears to be like to boost productiveness and digitization. We venture GDP to develop at 0.5% y/y in 2024, however then bounce again to 1.2% in 2025, nicely above potential progress. Inflation has been moderating, thanks largely to goods-price disinflation. However service costs are turning sticky. There are plaguing labor shortages in Japan, and wage positive aspects are prone to strengthen on this 12 months’s “Shunto” negotiations. Provided that companies are nonetheless passing increased prices to different companies, and in flip to clients (the companies element of the Producer Worth Index stays elevated at 2.1% y/y, and companies from insurance coverage to supply companions are reportedly elevating prices), we expect it might be unwise to take the present bout of disinflation at face worth. Inflation has slowed, however costs could possibly be stickier across the 2% deal with. Our consideration thus turns to the choices in entrance of the BoJ. Current commentary has aligned towards attainable motion if enough proof of a wage-price spiral emerges. That is already within the works, and with the upcoming wage negotiation knowledge anticipated to be stronger than final 12 months’s, we consider the BoJ will overlook the present damp progress prospects to finish the yield curve management framework and exit destructive interest-rate coverage by April. A weak restoration will underline a extra cautious tightening trajectory, though we don’t anticipate aggressive charge hikes simply but. Increased inflation structurally justifies increased nominal charges, nevertheless, actual charges in Japan have been steeped within the destructive. This has in flip helped to help progress. So, the BoJ’s steadiness right here is crucial-any charge hikes will push up actual charges, probably resulting in additional weak point. We subsequently anticipate substantial coverage tightening solely later within the 12 months, as soon as the restoration makes some headway. We anticipate enough ahead steering to underline any pullback in Japanese authorities bond purchases within the coming months.
What are the dangers?
All investments contain dangers, together with attainable lack of principal.
Mounted revenue securities contain rate of interest, credit score, inflation and reinvestment dangers, and attainable lack of principal. As rates of interest rise, the worth of fastened revenue securities falls. Low-rated, high-yield bonds are topic to larger worth volatility, illiquidity and risk of default.
Fairness securities are topic to cost fluctuation and attainable lack of principal.
Worldwide investments are topic to particular dangers, together with foreign money fluctuations and social, financial and political uncertainties, which might enhance volatility. These dangers are magnified in rising markets. Investments in firms in a selected nation or area might expertise larger volatility than these which are extra broadly diversified geographically.
Authentic Submit
Editor’s Observe: The abstract bullets for this text had been chosen by Searching for Alpha editors.
[ad_2]
Source link





