[ad_1]

by Fintechnews Switzerland
January 5, 2024
The rise of fintech is posing a menace to conventional monetary establishments, with these rising corporations encroaching on incumbents’ market share. That is evidenced by the opposed impression of fintech on the profitability of established monetary establishments, a brand new analysis by the Worldwide Financial Fund (IMF) discovered.
The findings, shared in a paper titled “Is Fintech Consuming the Financial institution’s Lunch?”, had been drawn from an evaluation of a cross-country database encompassing 10,167 monetary establishments and information on digital finance actions throughout 57 international locations. The research sought to realize insights into the connection between fintech and monetary establishments’ profitability and study the impression of the rise of fintech on banking sector.
Findings of the research reveal that established monetary establishments are witnessing a destructive impression on their profitability when the presence of fintech corporations is excessive, an impression that’s primarily pushed by diminished curiosity earnings as a consequence of heightened competitors within the lending market in addition to elevated prices.

Specifically, the research discovered {that a} 1% level enhance in fintech transaction volumes correlates with a discount of 0.09% factors in return on fairness (ROE) and a 0.02% factors decline in return on belongings (ROA) for incumbent monetary establishments. An evaluation of the transmission channels additionally uncovered a destructive impression on web curiosity margin (NIM), with a 1% level enhance in fintech transaction volumes prompting a 0.03% level lower in incumbent’s NIM.
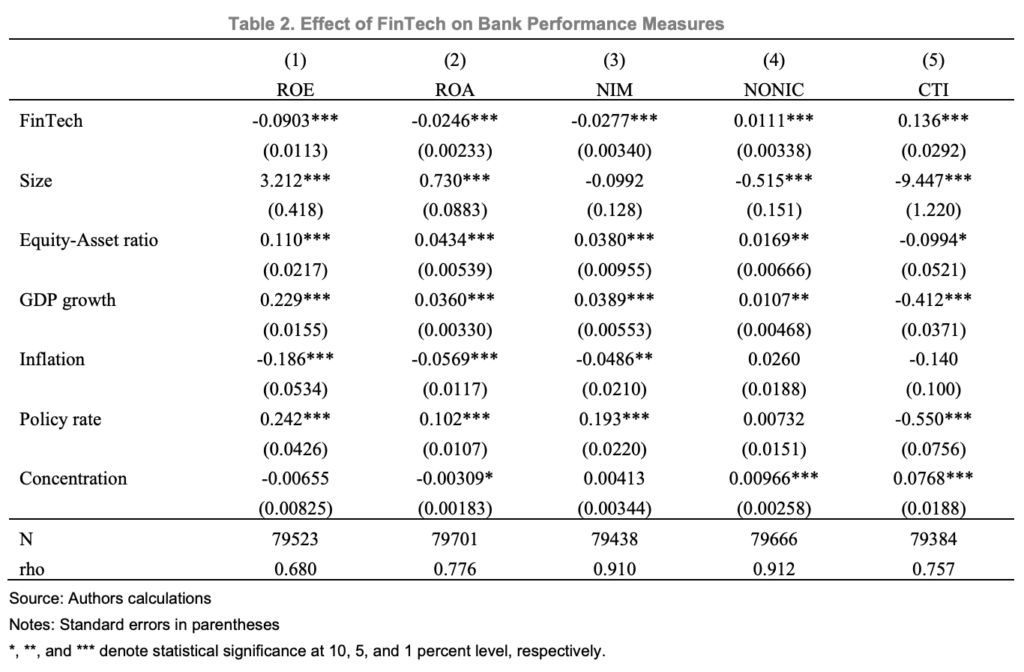
Impact of fintech on financial institution efficiency measures, Supply: Is Fintech Consuming the Financial institution’s Lunch?, Worldwide Financial Fund, Nov 2023
Moreover, fintech seems to have an opposed impact on incumbent’s value to earnings (CTI), with a 1% level enhance in fintech transaction volumes resulting in a 0.14% level enhance in incumbent CTI. Based on the IMF, this could possibly be attributed to the upper degree of IT investments required due to fintech strain. These prices are exacerbated by outdated legacy know-how, additional impacting profitability.
In parallel, the evaluation discovered that fintech has a constructive impact on non-interest earnings (NONIC), with a 1% level enhance in fintech transaction volumes being related to a 0.01% level enhance in incumbent NONIC. This outcome means that, though incumbents are responding to the extraordinary competitors by exploring new income streams, these efforts to diversify haven’t absolutely offset the profitability losses from fintech competitors.
Influence of various fintech enterprise fashions
Delving deeper into the fintech sector, the research discovered that totally different fintech fashions have various results on monetary establishments with cooperative banks tending to expertise larger revenue deterioration from P2P lending and steadiness sheet lending than bigger, extra advanced industrial banks.
Outcomes present that for a 1% level enhance in P2P lending transactions, cooperative banks are witnessing a 0.3% level lower in ROE. Likewise, an analogous enhance in steadiness sheet lending ends in a 0.2% level ROE lower. These outcomes are important provided that the median ROE for cooperative banks is 3.8%, the report notes.
Low revenue ranges for cooperative banks are attributed to diminished NIM and better CTI. A few of these establishments are dealing with challenges in affording IT investments and assembly digital banking expectations, probably limiting lending alternatives, the report notes. Fintech platforms, then again, can obtain economies of scale and broader geographical attain by leveraging know-how. Furthermore, these platforms could goal the identical untapped buyer segments that cooperative banks goal to serve.
In distinction to cooperative banks, industrial banks appear to be much less affected by fintech, probably as a consequence of their bigger measurement and wider geographical attain. In truth, the research discovered a constructive impact of the presence of P2P lending on the NONIC of economic banks, indicating potential advantages from collaboration with P2P lending platforms to increase income streams. Nonetheless, steadiness sheet lending was discovered to be a menace to industrial financial institution, impacting their NIM negatively.

Impact of fintech fashions on financial institution efficiency measures, Supply: Is Fintech Consuming the Financial institution’s Lunch?, Worldwide Financial Fund, Nov 2023
Disparities between markets
geographical traits and disparities, the research discovered that incumbents situated in markets with decrease financial institution focus, increased inventory market turnover, increased credit score depth, and better industrial financial institution profitability are extra vulnerable to dropping floor to fintech corporations.
Decrease financial institution focus suggests fewer entry obstacles for brand new fintech companies, and better inventory market turnover and credit score depth suggest extra aggressive and developed monetary techniques, indicating extra subtle traders, and entry to expert expertise. These circumstances are advantageous for fintech success however pose a menace to incumbent earnings, the report says.
On the institutional degree, incumbents with a decrease danger profile, together with decrease non-performing loans (NPLs), a decrease chance of insolvency, and better capital, are extra inclined to see their profitability decline due to fintech. It’s because monetary establishments with these traits are extra risk-averse and fewer inclined to lend, introducing alternatives for fintech companies to fill the gaps by serving as substitutes for conventional financial institution lending.
Lastly, the research discovered that in international locations with excessive regulatory high quality and authorities effectiveness, incumbent profitability tends to be positively impacted by fintech competitors. This means that well-designed laws can set up a degree taking part in discipline, enabling new fintech corporations to thrive whereas defending incumbents from unfair competitors practices.
Examine Suggestions
The report concludes by emphasizing the significance of ongoing monitoring of fintech improvement and its impression throughout the monetary system, noting that whereas fintech platforms are delivering advantages equivalent to enhanced effectivity in monetary service supply, elevated competitors, and improved entry to finance, the sector additionally presents challenges to incumbent establishments by limiting their revenue margins and eroding their market shares.
Consequently, banks could encounter difficulties in constructing capital buffers obligatory for absorbing losses and sustaining solvency. There may be additionally the potential for incumbents to interact in riskier lending and funding actions to protect market share and increase earnings.
These dangers and challenges require regulators to ascertain a correct framework that balances monetary innovation and systemic danger mitigation. The report proposes quite a few suggestions to broaden the regulatory scope and set up a degree taking part in discipline, advocating for the assessment and redesign of licensing regimes to embody new service suppliers throughout the regulatory framework the place acceptable, the implementation of extra sturdy capital, liquidity, and operational danger administration necessities tailor-made to the dangers posed by totally different fintech enterprise fashions, and the enhancement of the regulatory framework for smaller, much less technologically superior incumbents which are extra weak to fintech competitors.
The IMF additionally encourages incumbents to answer the rise of fintech and their rising menace by adjusting their enterprise fashions, specializing in enhancing value effectivity, diversifying earnings sources, consolidating operations, enhancing inner governance, and addressing problematic loans.
Featured picture credit score: edited from freepik
[ad_2]
Source link





